The ultimate goal of Biomedical sciences (BMS) is to understand the human body’s function in health and disease. Through biomedical research at molecular, cellular, organ and system levels, biomedical scientists expand our understanding of health and find ways to treat human diseases. Indeed, BMS is the heart of modern medicine. For example, during the global Covid-19 pandemic, biomedical scientists working behind the scenes in laboratories and research institutes were the key figures in creating the vaccines and diagnostics.
Working in a laboratory is the best way to learn how to do scientific research and development if you want to pursue a career in BMS. For that, we offer undergraduate students the opportunities to conduct biomedical experiments in our laboratories and interact with graduate students and faculty members. If you wantto learn more about the Biomedical Science major, admission, career opportunities, please come and visit our website. (https://www.cku.ac.kr/sites/life/index.do)
The objective of the Department of Biomedical Sciences is to produce health sector professionals capable of conducting and interpreting scientific projects intended to improve the understanding, diagnosis and treatment of human diseases. In particular, the training is aimed at developing the essential skills required for the acquisition and analysis of observations and experiments in biomedicine, while at the same time cultivating scientific robustness and integrity.
On successful completion of our program, each student is able to utilize tools required to acquire valuable data from biological samples, to design and conduct biomedical experiments, to analyze, write and evaluate data from the experiments and to present scientific observations clearly, verbally and in writing.
The purpose of BMS is to cultivate biomedical scientists who works with biological samples of health and disease. They are the professionals responsible for making solutions in healthcare. By analyzing and working with biological samples with strong research and problem-solving skills, they invent new ways to overcome current health-related problems. For that, we guide students in accessing information after ensuring they learn basic concepts in biomedical sciences.
Typically after graduation with solid background in laboratory work, they are employed in national health organizations, private and public hospitals, pharmaceutical companies, research centers, universities or intellectual property law firms.
BMS offers the Bachelor of Science degree in Biomedical Sciences. Students follow a curriculum that includes general education courses, major courses, and Capstone courses. BMS curriculum consists of human-oriented basic science courses that can be tailored to an individual’s career interests. The curriculum is designed to be flexible so as to meet the needs of all students, regardless of which healthcare-focused career program they plan to pursue (e.g., biomedical research, medicine, dentistry, pharmacy, engineering, public health, etc.). Most of the coursework is synchronous and requires in-person class attendance, our courses.
All students are required to complete a minimum of two-year of course for diverse biomedical experiments. These include Cell Biology, Microbiology, Molecular Biology, Molecular Genetics, Analytic Technology, Fermentation Engineering. This culminates during the sophomore and junior year with students working approximately 10 hours per week in their labs. Most Biomedical Science students begin working in a lab during the first semester of their junior year.
A crucial and innovative component of the curriculum is the Capstone course which support students’ Capstone Projects. The Capstone course is a structured longitudinal learning experience that empowers you to conceptualize an idea you are passionate about that identifies a problem in healthcare or the biomedical sciences, develop and implement a Capstone Project to solve that problem during the time you are enrolled in the program, and disseminate your results. You will lead this project as the principal investigator and work with a mentoring team to coach you every step of the way. During 6th and 7th semesters, the Capstone course director will provide milestones to keep you on track towards completing your project within the program’s plan of study timeline. The Capstone Project requires that you prepare and deliver a final presentation to the program and provides the opportunity to submit a research or review article summarizing your completed project.
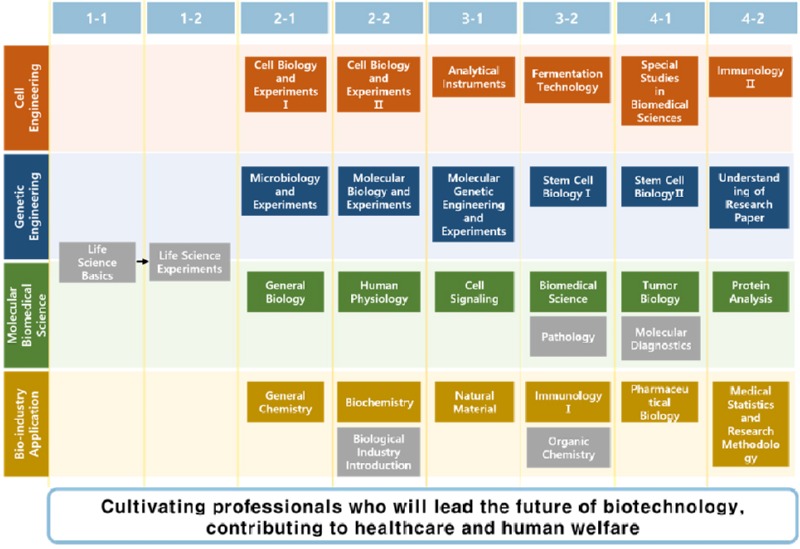
In the field of biomedical sciences, the major subjects cover various Areas related to biology and medical science. These courses aim to provide a solid foundation in the basic theories of life science. Through a combination of theoretical knowledge and hands-on laboratory experiments, students enhance their understanding and completeness of knowledge. The curriculum is specialized based on research Areas, such as natural pharmaceuticals, clinical medicine, and cell therapy/regenerative medicine. Fundamental disciplines like biochemistry, molecular biology, cell biology, microbiology, immunology, natural product chemistry, and stem cell biology are covered, along with in-depth studies in applied disciplines such as toxicology, bioinformatics, genetic engineering, and experimental animal science. This comprehensive learning approach equips students with diverse knowledge necessary for research and technological development in the field of biomedical sciences.
General Biology 1,2
Biology is a discipline that studies the essence and characteristics of living organisms, as well as the laws governing the manifestation of life phenomena. In conjunction with the content of General Biology and Experiment 1, this course aims to discuss the structure and function of animals and plants, as well as various life activities. It also intends to explore interactions in ecosystems and the role of humans based on understanding. Additionally, through experiments and practical work, the course aims for an in-depth understanding of the content.
General Chemistry
This course aims to facilitate an understanding of the structure and properties of substances and their interactions at macroscopic and microscopic levels. The knowledge acquired during the exploration of substances is applied to specialized judgments in the major field and daily life. The curriculum is based on the fundamental concepts and laws of chemistry, quantum mechanical understanding of atomic structure and chemical bonding, and the identification of forces between liquids, solids, and molecules. Practical applications through experiments are emphasized.
Biochemistry 1,2
Understanding the chemical mechanisms at the molecular level to maintain life phenomena is the focus of this course. It covers the structure and catalytic action of biomolecules, the three-dimensional structure of amino acids and proteins, an understanding of enzymes, and the structure and components of biomolecules such as lipids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and cell membranes.
Cell Biology and Experiment 1,2
Cell biology forms the foundation of modern biology. Through this course, students acquire basic knowledge of cell structure and function, cellular metabolism, the utilization of genetic information, and intracellular signal transduction. The course is centered around the textbook "The World of the Cell" and utilizes multimedia resources for comprehensive teaching.
Microbiology and Experiment
This course introduces the diversity of microorganisms and aims to familiarize students with the cellular structure and metabolic processes of microorganisms compared to higher organisms. Topics include the biochemical aspects of microbial nutrition, metabolism, synthesis, and the structure and function of macromolecules and genes that constitute microorganisms.
Molecular Biology and Experiment
This course covers the essence and origin of life, energy metabolism in living organisms, the composition and structure of nucleic acids, and the methods and applications of molecular biology. Topics include DNA replication, the driving force behind evolution such as mutation and DNA damage repair, and the basic processes and regulation of gene expression.
Human Physiology
The course explores the regulation of life phenomena in response to internal and external environmental changes, focusing on the nervous system's electrochemical control of homeostasis. Topics include material transport through cellular membranes, the electrochemical characteristics of nerve cells, signal transmission between nerve cells, and the regulation of motor functions in the spinal cord, brainstem, cerebellum, and cerebral cortex.
Immunology
This subject aims to understand the biological structure and function of tissues and cells that make up living organisms at the molecular level. It focuses on the molecular structure and function of macromolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and carbohydrates, as well as the enzymatic catalysis of biochemical reactions and the mechanisms of action and deactivation of enzymes.
Pathology
The course explains the causes of diseases, the mechanisms of disease development, and the morphological and functional changes in organs. It also provides education on the technical methods used in pathology for application in clinical settings.
Analytical Instruments and Experiment
Building on cell biology and microbiology, students learn the principles of the operation of various instruments and how to interpret the results of experiments using these instruments.
Cell Signaling
Students learn the major pathways of intracellular signal transduction and the classification of factors, along with experimental studies related to cell signaling.
Toxicology
This subject studies the fundamental principles of toxicology, its historical background, the mechanisms of toxic action, and the final goal of protecting humans from toxic substances. It covers toxic substances (e.g., carcinogenic, mutagenic, teratogenic, organ-specific toxic substances) and their roles in the disease development process.
Molecular Genetic Engineering Experiment
The goal of this course is to acquire basic knowledge necessary for the industrial and medical applications of genes. It covers the fundamental principles of genetics, gene manipulation techniques, and the regulatory mechanisms of gene expression.
Tumor Biology
Cancer research holds significant importance in the field of modern life sciences. This course comprehensively covers topics related to cancer, understanding its causes, progression, and mechanisms for the development of effective prevention, diagnosis, and treatment technologies.
Natural Products Pharmacology
This course covers the study of secondary metabolites produced by organisms in nature and their functions and applications, including isolation, analysis, and more.
Molecular Diagnostic Medicine
Building on an understanding of molecular biology, this course covers specimen collection, molecular diagnostic techniques using nucleic acids, equipment used in molecular diagnostics, and diseases applicable to molecular diagnostics.
Systems Biology
This course explores biological information such as genes, proteins, and metabolites using applied mathematics, information science, statistics, computer science, and artificial intelligence. It aims to cultivate specialized knowledge in future medicine based on biological information and practical education for information processing technology in the big data produced in the field of biomedical science.
Stem Cell Biology
This course studies the characteristics of stem cells with self-renewal ability and the potential to differentiate into various cell types, with a focus on their application in regenerative medicine.
Undergraduate Thesis Seminar in Biomedical Science
This seminar course is designed for undergraduate students majoring in biomedical science. Students present the results of literature research and experimental research for their undergraduate thesis, gaining practical experience in writing papers and presenting seminars. The course introduces the ongoing research in professors' labs, allowing students to accumulate knowledge about research conducted within the university.
Specialized Research in Biomedical Science 1,2
This course provides an opportunity for students to learn and practice the understanding of biomedical science and gain practical knowledge and skills through experiments. Students develop hypotheses, design experiments, and conduct relevant experiments to produce data for their graduation or academic papers.
Field Internship
The goal of this course is to provide opportunities for students to enhance their practical research capabilities by acquiring the principles of experiments and participating in direct experiments.